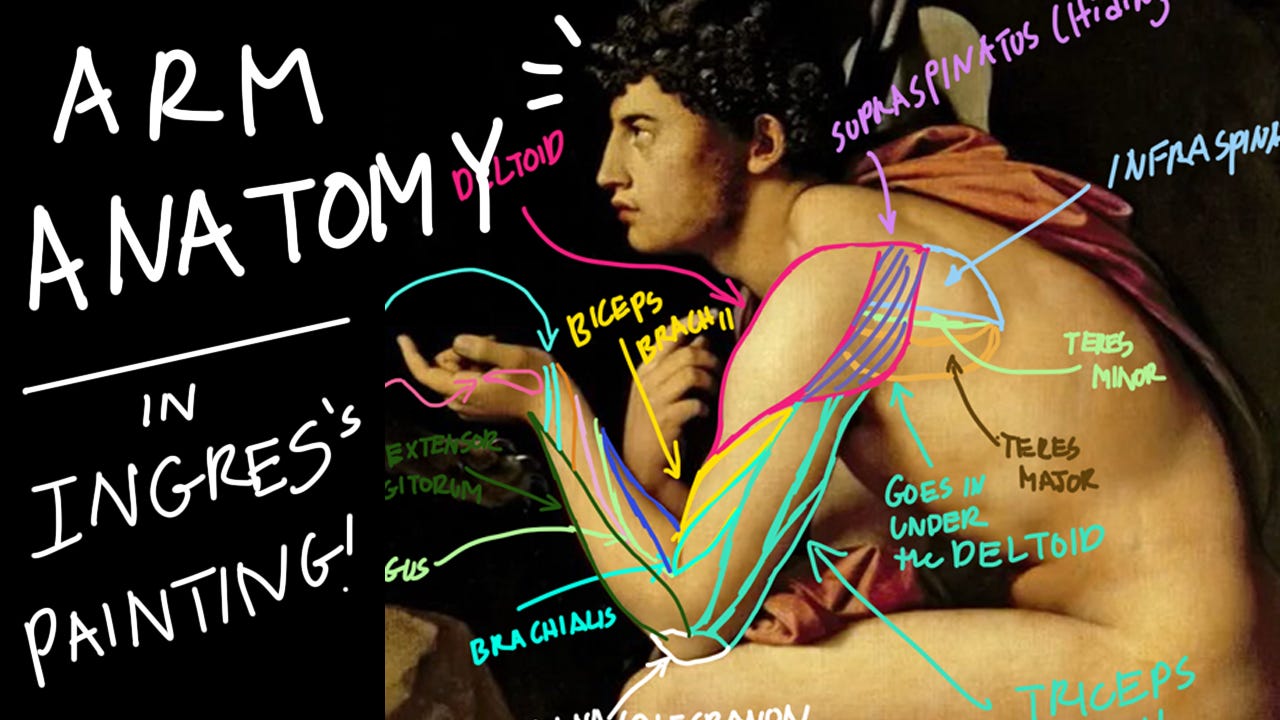
Learning Arm anatomy from Ingres's painting
Finding the muscles in the arm!
Learning the Anatomy of the Arm.
I’m super excited to share some tips and advice on learning Anatomy and I’ve been in the crave of discovering more about where the muscles are placed and also their functions and what each muscle does.
So we’re going to analyze and learn the arm muscle by tracing it out from one of Ingres’s paintings.
The painting we’ll be looking at is:
"Oedipus and the Sphinx" by Jean Auguste Dominiques Ingres
How to learn and understand Anatomy?
3 main things that will help learning Anatomy a lot easier and more enjoyable. Making you excited and curious about it.
Structure of the Muscle. What does the shape of the muscle look like and how it’s built and constructed? As we add all the muscles together
Placement of the Muscle. Where is each muscle placed? And where does it attach to and where does it start and end?
Function of the muscle. What does this muscle do? What movement does it make us move our body? Does it pull in or extend out?
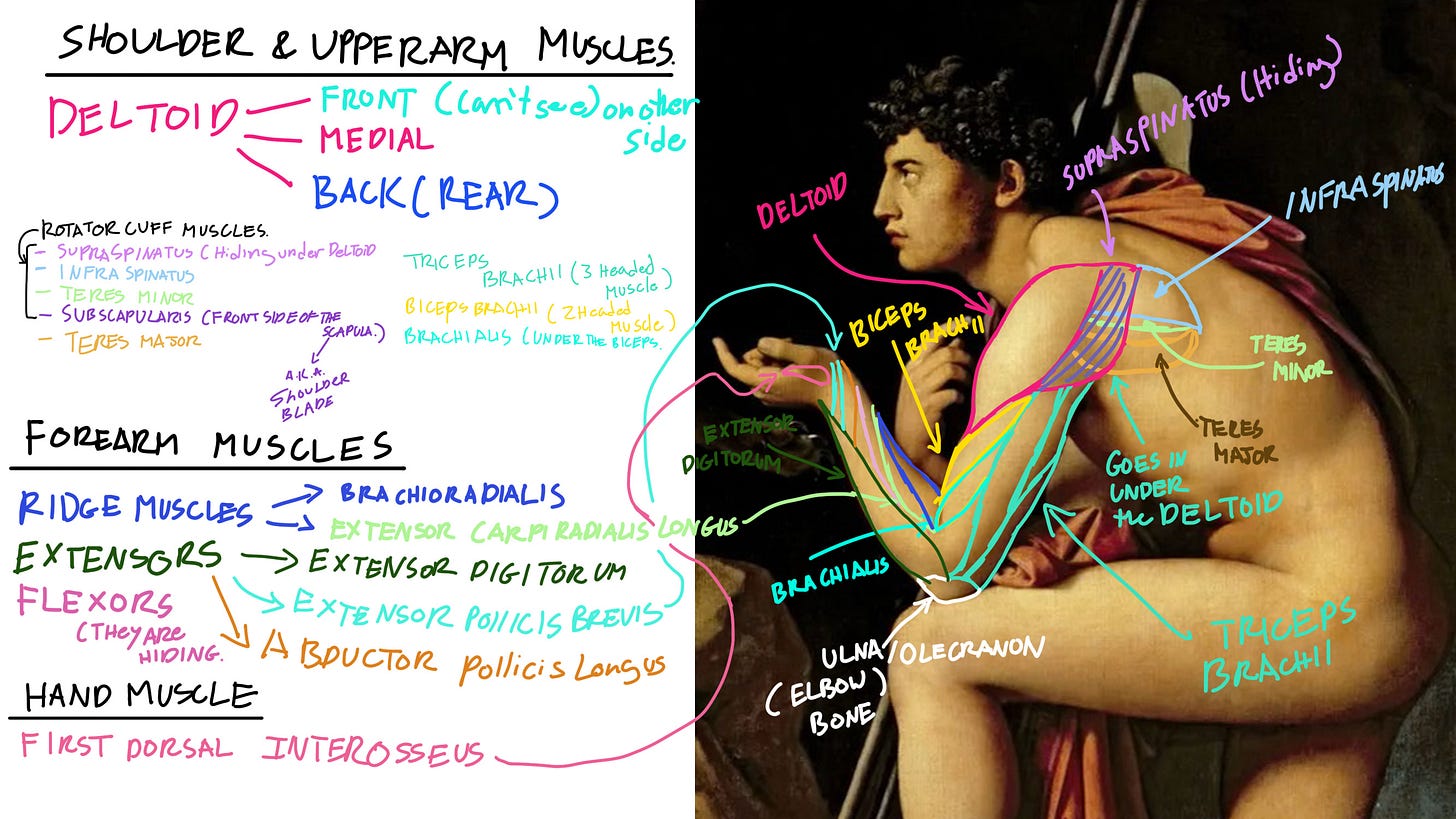
Upper Arm Muscles
We’re going to learn the muscles we see in the Upper Arm area (Only the ones that are visible on this side of the arm.):
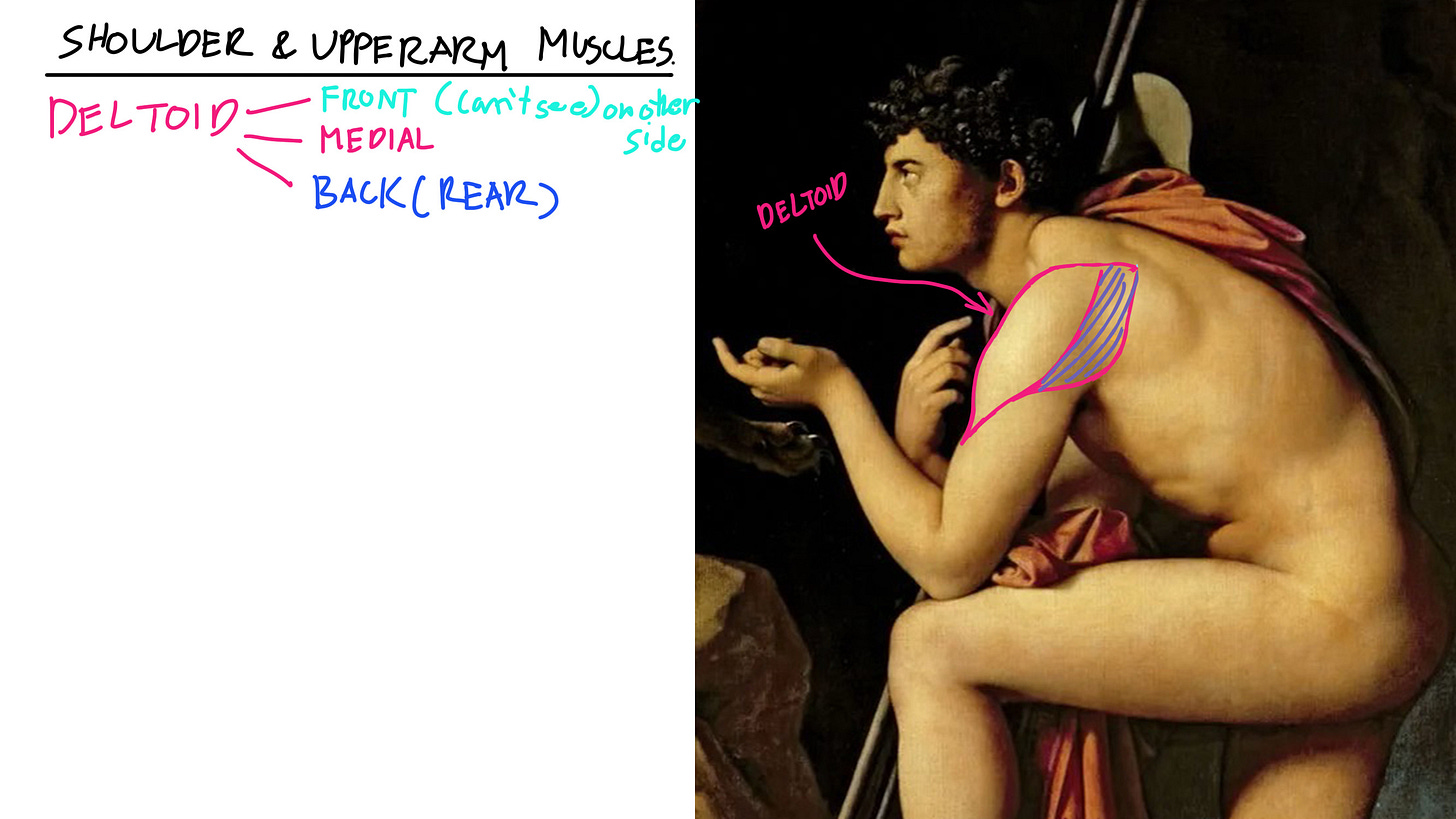
Deltoid = The Deltoid is this leaf-like shape or more precise a upsidown raindrop shape. Since it’s divided into 3 main parts.
The Front, Medial, and Back (Rear)
The Deltoid helps us lift and raise our arms up and back down.
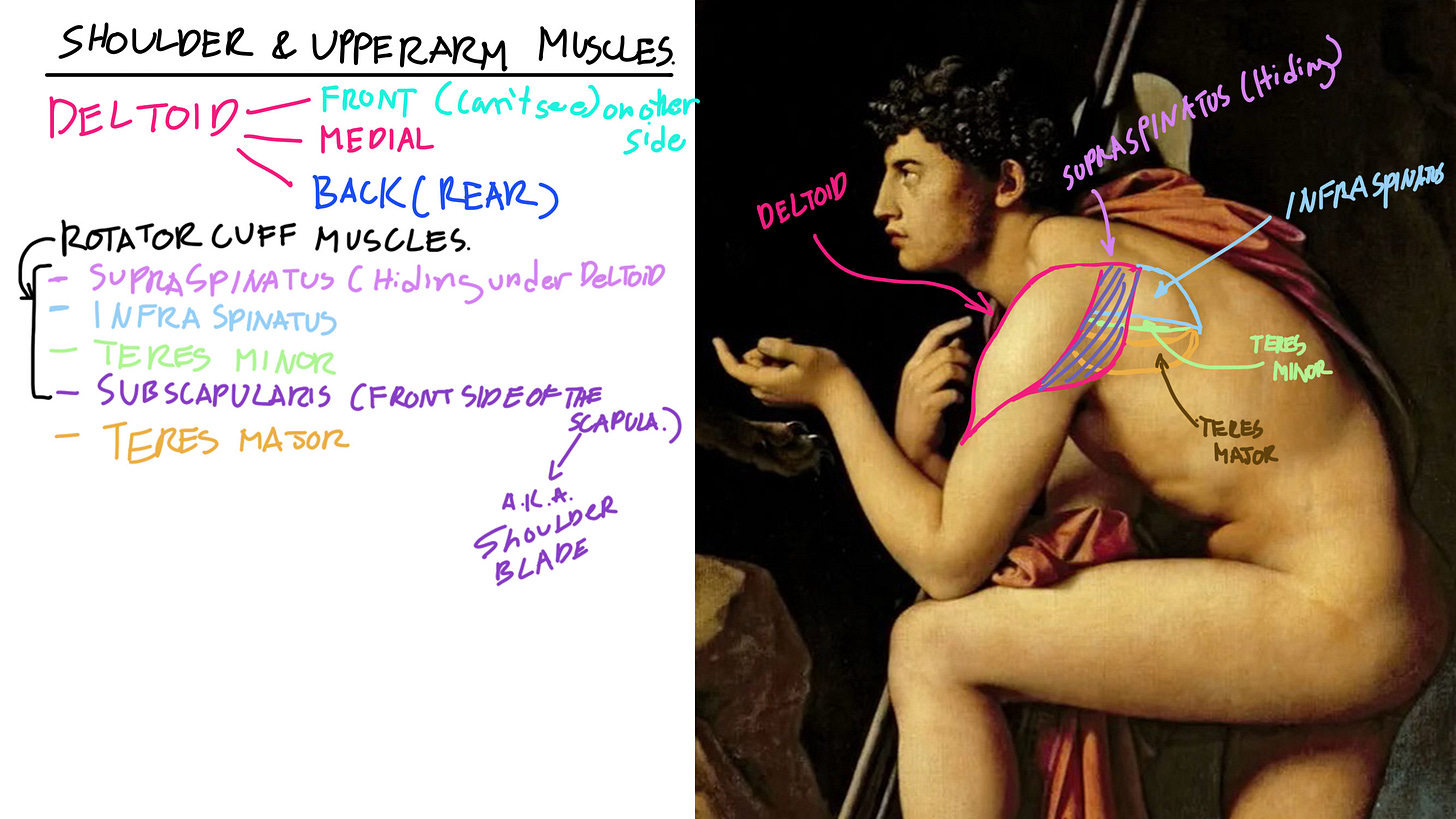
Shoulder Muscle
Also known as the “Rotator cuff muscles” have 4 main muscles: These muscles help our arm and shoulder swing backward and also rotate our upper arm outwards.
Supraspinatus = We can’t see this muscle because it’s hiding under the Deltoid and one of the back muscles. It’s on the other side of the spine of the Scapula (A.K.A. Shoulder blade)
Infraspinatus = Is the larger muscle of the rotator cuff muscles. It’s on the opposite side of the spine of the scapula. and part of it hides under the Deltoid.
Teres Minor = is tucked under the Infraspinatus. A deeper muscle of the rotator cuff muscles.
Subscapularis = This muscle is located on the front side of the Scapula. So we can’t see it on this side.
We also have another muscle below the Teres minor which is called the Teres Major.
Teres Major = This muscle is attached from the back side and lower part of the scapula to the front part of the Humerus (the bone of the upper arm)
This muscle also helps rotate our arms inwards and lift our arms out to the side and backward.
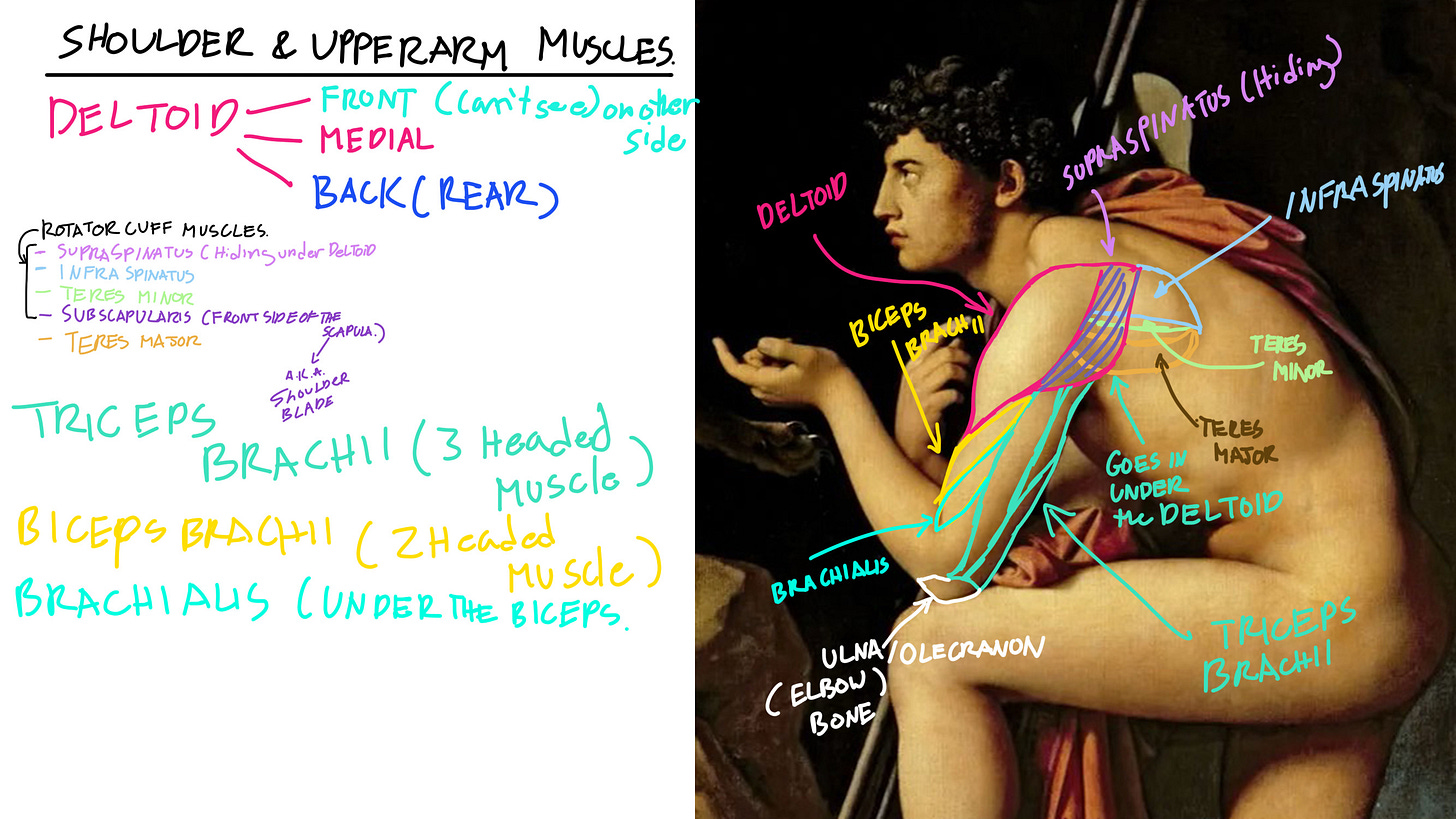
Triceps
The Triceps called “Triceps Brachii” Is located at the back side of the upper arm. It’s a 3 headed muscle. One that attaches to the shoulder blade (Scapula) and two that attaches to the Humerus (Upper arm bone). This muscle has 3 main functions. It moves our elbow up and down. Raise our whole arm all the way up. Help our elbow/forearm swing back and forward.
Biceps
The biceps is a 2 headed Muscle. The top part connects to the Acromion (Tip part of the Scapula) and has a tendon that runs in between the top bone of the Humerus.
This muscle helps us bend our elbow and bring the forearm up. So when you see people flex and show those showy biceps muscles. This is that muscle and we call it the Biceps Brachii.
Brachialis is a neighbor muscle that hides under it and helps support and make the biceps brachii bigger and more pumped outwards. It also helps move the forearm up.
Forearm Muscles
The forearm muscles are divided into 3 main muscle groups:
Ridge Muscles = Has 2 main muscles. The Brachioradialis (Which is on top of the Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus. These two muscles help flex the elbow and also turn your forearm from the back of the hand and rotate it so that your palm is facing downwards.
Extensor Muscles = Extensor Digitorum, Extensor Pollicis Brevis, Abductor Pollicis Longus. These muscles help your wrist extend and bend backward and also bend back your thumb.
Flexor Muscles = Which is on the belly side of the forearm that help bend your wrist inwards.
Thumb Muscle
The first dorsal Interosseus = Is the meaty thumb muscle you see on the back side of your hand. Not the palm side. This muscle helps move your index finger out and in.
Mini Exercise for you!
Draw the arm and the muscle placement of the whole arm. This will help you remember better and understand where each muscle goes and also remember the names and their functions.
Have fun learning the first few muscles of the arm!
What did you discover?
I’m curious to see what your thoughts are on the arm anatomy we see in Ingres’s painting. If you also discovered something new, I would love to know! (You can comment and share your thoughts below!)
Thank you for reading my fun little discovery and I hope you also get to learn and share your discoveries too!
You can also share it with fellow friends, artists, and cellists of today's Victoria Yu Art on social media, forward it to someone who might benefit, or text it to a friend. Thanks for reading!
PS Feel free to watch my new YouTube video about this new post! Sharing thoughts and ideas!




Excellent art anatomy tutorial Victoria!